✔ 100% Authentic Product
👁️ Currently Viewing 3466
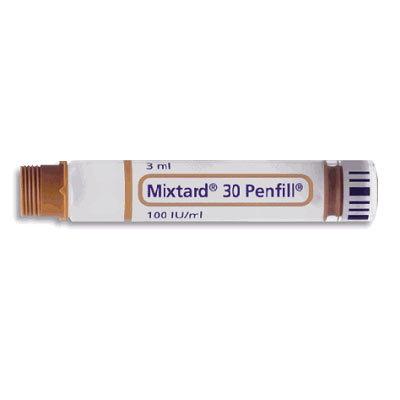
Mixtard 30 Penfill 100IU/ml
Injection.
Generic Name: Biphasic isophane insulin Inj. (human
monocomponent) 30% soluble insulin & 70%
isophane insulin; 100 i.uJrnl with penfill.
Manufacturer/Distributor: Nordisk/Transcom
🚚 তাপমাত্রা নিয়ন্ত্রিত ডেলিভারি: এই পণ্যটি গুণগত মান বজায় রাখতে শুধু মাত্র ঢাকা শহরের ভিতরে আইস ব্যাগ এর মাধ্যমে ডেলিভারি করা হয়।
Discount
Price: ৳ 500
MRP:
৳
510
2%
Off

100% Genuine Products, Guaranteed

Safe & Secure Payments, Always

Fast, Secure & Efficient Delivery

Proper Packaging
 Cash on Delivery - All over Bangladesh
Cash on Delivery - All over Bangladesh Regular Delivery - 12-24 Hours, Dhaka City* Charge Tk.39-59
Regular Delivery - 12-24 Hours, Dhaka City* Charge Tk.39-59 Regular Delivery - 24-48 Hours, Other Cities* Charge Tk.99-110
Regular Delivery - 24-48 Hours, Other Cities* Charge Tk.99-110
 ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ৯৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকা
শহরে
ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ৯৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকা
শহরে ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ২৯৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকার
বাহিরে
ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ২৯৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকার
বাহিরে
100% Genuine Products, Guaranteed
Safe & Secure Payments, Always
Fast, Secure & Efficient Delivery
Proper Packaging
 Cash on Delivery - All over Bangladesh
Cash on Delivery - All over Bangladesh Regular Delivery - 12-24 Hours, Dhaka City* Charge Tk.39-59
Regular Delivery - 12-24 Hours, Dhaka City* Charge Tk.39-59 Regular Delivery - 24-48 Hours, Other Cities* Charge Tk.99-110
Regular Delivery - 24-48 Hours, Other Cities* Charge Tk.99-110 ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ৯৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকা
শহরে
ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ৯৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকা
শহরে ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ২৯৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকার
বাহিরে
ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ২৯৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকার
বাহিরে
✅ Description:
Indications
All people with type 1 diabetes should be treated. Diet and/or oral hypoglycemic medications are ineffective in treating patients with type 2 diabetes.
Patients with diabetic ketoacidosis, hyperosmolar non-ketotic syndrome, and diabetic patients who are under stress from serious infections or extensive surgery. Diabetic pregnancy treatment
Pharmacology
The recombinant human insulin (rDNA) is a human insulin produced by recombinant DNA. Has the same function as natural insulin in terms of its structure and composition Hepatic, skeletal muscle, and adipose tissue are all stimulated to take in and use glucose by insulin. Blood glucose levels are also lowered when glycogenesis and gluconeogenic activity are increased.
30% human insulin and 50% human insulin (rDNA) Starts working within 30 minutes of injection, reaches a peak within 2-8 hours, and lasts approximately 24 hours
Dosage & Administration
The average range of total daily insulin requirement for maintenance therapy in type 1 diabetic patients lies between 0.5 and 1.0 IU/kg. In pre-pubertal children it usually varies from 0.7 to 1.0 IU/kg, whereas in insulin resistant cases, e.g. during puberty or due to obesity, the daily insulin requirement may be substantially higher. Initial dosages for type 2 diabetic patients are often lower, e.g. 0.3 to 0.6 IU/kg/day.
The dosage form, the dosage and the administration time of the insulin are different due to the individual differences of each patient. In addition, the dosage is also affected by food, working style and exercising intensity. Therefore, patients should use the insulin under doctor's instruction.
An injection should be followed by a meal or snack containing carbohydrates within 30 minutes. Injection is administered subcutaneously in the upper arm, thigh, buttock or abdominal wall. A subcutaneous injection into the abdominal wall results in a faster absorption than from other injection sites. Insulin Human (rDNA) 30/70 & Insulin Human (rDNA) 50/50 are never to be administered intravenously.
Preparation before use:
Clean your hands.
Shake or rotate the vial gently to mix the solution uniformly and check if the insulin has the normal appearance.
In case of using a new vial, flip off the plastic protective cap and wipe the rubber plug with an alcohol swab.
Draw air into your syringe equal to the amount of insulin needed.
Puncture the needle into the vial and inject the air.
Turn the bottle and syringe upside down and withdraw correct dose of insulin into the syringe.
Before pulling out the needle, check if there are any bubbles remain in the syringe. If so, put the syringe upright and tap the syringe to discharge the air bubbles.
Injection site:
Choose the area where skin is less tight, such as the upper arm, thigh, buttock or abdomen.
To avoid tissue damage, choose a site for each injection that is at least 1 cm from the previous injection site.
Injection method:
Cleanse the skin with alcohol where the injection is to be made.
Put the needle in such a position as to form 45° angle with the skin.
Puncture the needle into skin and inject insulin.
Keep the needle under the skin for at least 6 seconds to make sure the entire dose is injected.
Pull the needle out and apply gentle pressure over the injected site for several seconds.
Do not rub the injection site.
Interaction
To counteract the rise in blood glucose caused by oral contraceptive medicines such as adrenal corticosteroids, thyroid hormones, etc., you may need to increase the amount of Insulin. Reduce insulin dosage when using hypoglycemic medications, such as salicylate, sulfanilamide, and other anti-depressants.
Contraindications
Insulin-induced hypoglycemia or an allergic reaction to insulin or any of its excipients.
Side Effects
Symptoms of hypoglycemia, the most prevalent side effect of insulin therapy, can appear unexpectedly. Allergic reactions such as redness and swelling or itching have been recorded seldom. After a few days, it normally goes away by itself. However, in rare cases the allergy to insulin may be caused by something else, such as a cleaning agent or improper injection technique.
Pregnancy & Lactation
As insulin does not pass through the placental barrier during pregnancy, there are no limits on using insulin to treat diabetes during pregnancy. The infant is not at risk from the mother's insulin medication.
Precautions & Warnings
Particularly in type 1 diabetes, inadequate dose or withdrawal can lead to hyperglycemia. As a result of an insulin dose that is too high compared to the insulin need, hypoglycemia can occur. An unanticipated, vigorous physical activity or skipping a meal can cause hypoglycemia.
Therapeutic Class
Medium Acting Insulin
Storage Conditions
2°C to 8°C in the fridge Be careful not to become paralyzed. Insulin that has been used recently does not need to be refrigerated, but it should be kept in a cool, dark place away from heat and light. A month's supply of insulin can be stored at room temperature.
⚠️Disclaimer:
At ePharma, we’re committed to providing accurate and accessible health information. However, all content is intended for informational purposes only and should not replace medical advice from a qualified physician. Please consult your healthcare provider for personalized guidance. We aim to support, not substitute, the doctor-patient relationship.